|
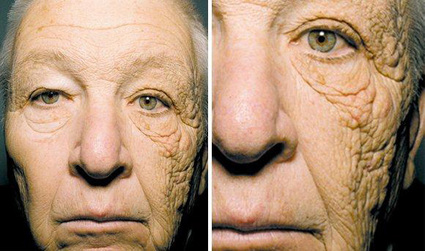
Photoaging is changes in the skin induced by long-term ultraviolet ray (UV) exposure. When illuminated with UV, a substance called collagenase is activated and collagen is broken down. Accumulation of this process for a long time causes spots and flabbiness on the skin. But the effect of UV is not only spots and flabbiness on the skin.
What increases these days is base-cell carcinoma. When illuminated with UV, DNA of the skin cells is damaged. If the damaged cells are repeatedly divided, skin cancer occurs. Langerhans cells are immune cells protecting the body from viruses and others. When they are illuminated with UV, the number of Langerhans cells decreases so the function of the immune system becomes weaker. Pitfalls of countermeasure against UV There are two 50’s females who pay attention to prevent UV, wearing sunscreen and using a parasol when they go outside. But there is a big difference about the quantity of collagen under the skin between these two females. If you keep being exposed to UV, breakdown of collagen is progressed. That makes the difference about photoaging. What makes the difference about photoaging between these two females? 1. Movement of the Sun and pattern of behavior in the house The female A whose photoaging is not progressed moves at the other side of the Sun. on the other hand, the female B whose photoaging is progressed moves in the room getting sunlight. There are two types of UV. UVB mostly doesn’t pass through windows, but UVA passes through windows and pours into a room. UVA doesn’t make the skin red so there can be exposure to a large amount of UVA without notice. The female B is likely to be exposed to a large amount of UVA in the house. 2. How to use a parasol UV comes from all the directions by reflection. If you use a parasol at the high position, you can’t prevent UV coming from sides and below. While the female A whose photoaging is not progressed use a parasol at lower position, the female B whose photoaging is progressed use a parasol at high position. This makes big difference about UV strength around their faces. Also the female A whose photoaging is not progressed changes the direction of her parasol to make it face direct sunlight.(Fig. 1) Quiz for UV measure Q1. Which place has the strongest UV? (A) On the sea shore (B) At the top of a mountain (C) In the city A1. (B) At the top of a mountain Since the altitude on the top of a mountain is high, the air is clear, containing less dust and fluff in the air so that UV is not absorbed. That makes UV strong at the top of a mountain. Q2. Being by the window exposes you to UV. Which can prevent UV more? (A) Closing only the window (B) Closing only the lace curtain A2. (A) Closing only the window Windows absorb most UVB which becomes a cause of sunburn and skin cancer. Closing both the window and lace curtain is more effective. (UV intensity in the experiment: Only window 0.86, Only curtain 1.30, Both 0.18) Q3. It is important to choose the material of clothes to protect the skin from UV. Which material doesn’t pass UV most? (A) Cotton (B) Silk (C) Polyether A3. (C) Polyether Polyester absorbs UVB which is most dangerous to the skin. But polyester doesn’t absorb sweat so it is recommended to wear mixed material of cotton which absorbs sweat and polyester which absorbs UVB.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
IchiroThis Blog is for a memo of my clinical realizations, information about health I have learned recently and update information. Archives
April 2024
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed